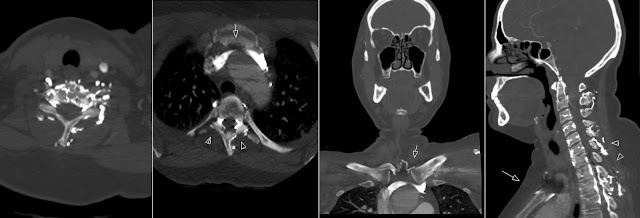
Skull Fracture Line

This very thin skull fracture line without dislocation can be easily missed. It is hard to find on the axial images, well seen on the sagittal projection and easy to find on the 3D reconstructions. So my simple radiology tip is: "Look at all images".